Selection Criteria for αSTEP and Stepper Motors Have Been Reviewed
Thank you very much for your continued patronage of Oriental Motor products.
The selection criteria for αSTEP and Stepper Motors have been changed as follows.
Changes
- Acceleration/Deceleration Rate
To be excluded from the judgment criteria (The value restriction will be removed). - Inertia Ratio
Guideline for 30 times or less of rotor inertia.
Before the Change
| Applicable Products | Motor Section Frame Size [mm] | Acceleration/Deceleration Rate TRS [ms/kHz] |
|---|---|---|
| αSTEP | 20, 28, 42, 60, 85 | 0.5 min. |
| 5-Phase Stepper Motors | 20, 28, 42, 56.4, 60 | 20 min. |
| 85 | 30 min. | |
| 2-Phase Stepper Motors | 20, 28, 35, 42, 50, 56.4, 60 | 50 min. |
| 85 | 75 min. |
Before the Change
| Applicable Products | Motor Section Frame Size [mm] | Inertia Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| αSTEP | 20, 28, 42, 60, 85 | 30 max. |
| 2-Phase/5-Phase Stepper Motors | 20, 28, 35 | 5 max. |
| 42, 50, 56.4, 60, 85 | 10 max. |
After the Change
| Applicable Products | Motor Section Frame Size [mm] | Inertia Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| αSTEP | 20, 28, 42, 60, 85 | 30 max. |
| 2-Phase/5-Phase Stepper Motors | 20, 28, 35 | 30 max. |
| 42, 50, 56.4, 60, 85 | 30 max. |
*A large inertia ratio may affect the settling time.
Reason for the Change
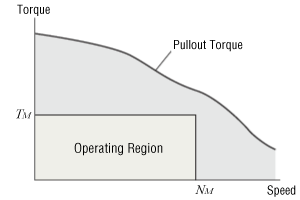
The αSTEP and stepper motors are represented by the operating speed NM and required torque TM If the operating area is within the pullout torque, the desired equipment can be operated. Oriental Motor has provided reference values for acceleration/deceleration rates and inertia ratios to ensure the selected motor operates more reliably.
- Acceleration/Deceleration Rate
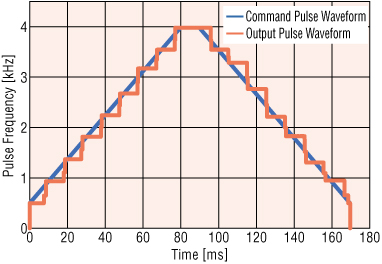
The pulse signal output by the pulse generator, the pules speed changes in a stepped during acceleration/deceleration, with the pulse speed step becoming larger as the acceleration or deceleration becomes more abrupt.
Pulse generators around the early 1990s, when the above standards were set, had products with large pulse steps during acceleration/deceleration. (Refer to Figure 1)
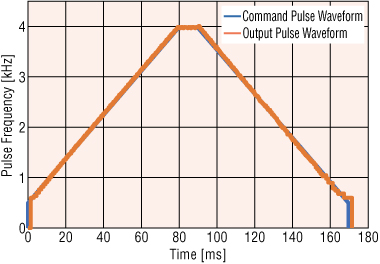
However, current pulse generators are capable of smooth output with fewer steps. (Refer to Figure 2) - Inertia Ratio
In reviewing the criteria for acceleration/deceleration rates, repeatedly tested operation at high inertia ratios using the existing pulse generator and driver.
As a result, it was confirmed that even 2-phase/5-phase stepper motors can operate with an inertia ratio of 30 times without problem as long as the safety factor is maintained.
Based on the above points, reviewing the criteria for selecting more optimal motors.