Think Through Product Usage
Reducing Power Consumption Using High Torque Stepper Motors
Effective use of high torque motors can reduce power consumption. After revising the magnetic design and structure design of the PKP Series stepper motors, it produces much more torque than conventional products of the same size. In addition, torque can be increased in the high-speed range by using high current motors. Drivers that maximize the performance of the PKP Series are also available.

PKP Series (2-Phase/5-Phase)

Driver for 5-Phase Stepper Motors
CVD Series
The Effects of Using the PKP Series
Speed - Torque Characteristics and CO2 Emissions Comparison
The high torque of the PKP Series can be utilized to achieve the operating current value with the same torque as a conventional product to reduce CO2 emissions.
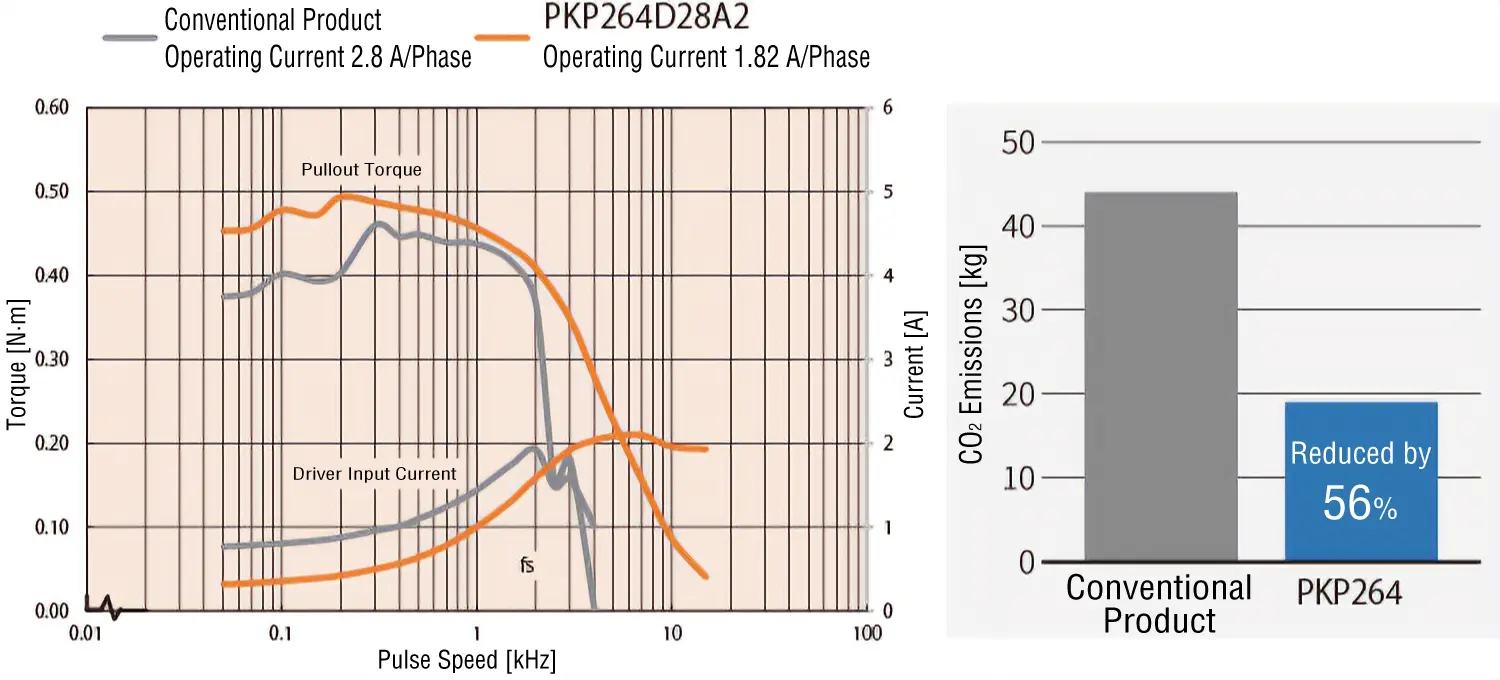
- For comparison between PK264D28A and PKP264D28A2
| Speed | 0.1 kHz (30 r/min) |
|---|---|
| Load Torque | no load |
| Operating Time | 24 hours a day, 365 days a year |
| Operation Conditions | 50 % operating, 50 % stand by |
| Power Supply Voltage | 24 VDC |
| CO2 Coefficient | 0.453 kg-CO2/kWh |
CO2 Emissions
Reduced by up to 56 %
Comparison of Motor Temperature Rise
Temperature rise in the motor can be suppressed by lowering the operating current value in the PKP Series. This increases the life of the motor.
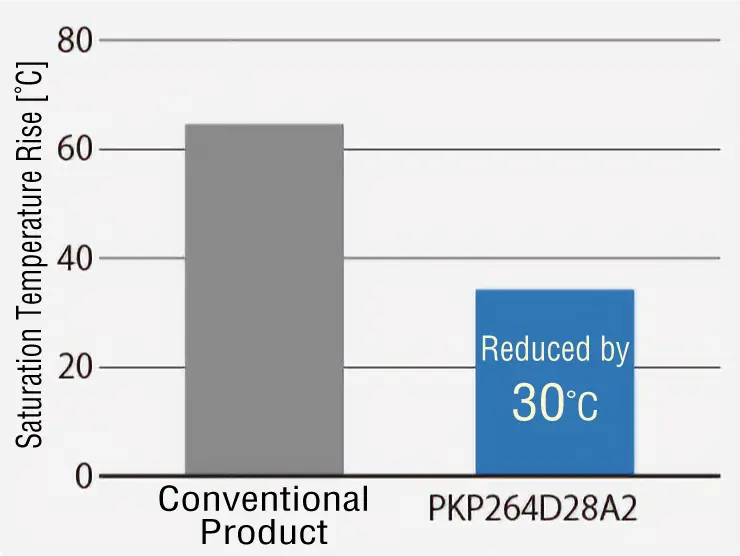
| Saturation Temperature Rise [℃] |
|
|---|---|
| Conventional Product | 64.6 |
| PKP264D28A2 | 34.2 |
Temperature Rise
Decreased by 30 °C
Compatible Products

Stepper Motor PKP Series
High torque and low vibration 2-phase stepper motor with a basic step angle of 1.8˚ (resolution of 200 steps per revolution). A wide variety of products are available for selecting a motor that meets your design specifications. (A separate dedicated driver is required to operate each motor.)

Driver for Stepper Motor
CVD Series
These are drivers with DC input for driving 2-phase stepper motors and 5-phase stepper motors. A microstep function has been added to the driver with a low vibration design to achieve drive with even lower vibration. 3 types of drivers are available to choose from depending on the mounting method and cable pull-out direction.