Please Tell Me About the Protective Equipment for the Motor!


-

Ms. Ori, please explain! We received an inquiry from a customer who wanted to know the current value of protective equipment for an AC motor, but I don’t know much about protective equipment…
-

Did you ask what they want to protect? There are several types of protective equipment and the current value you answer depends on the answer.
-

He said it was for a motor.... Are there many different kinds? I’m sorry. I didn’t check with him thoroughly.
-

Next time if there’s an inquiry, it would be great if you could ask the customer. Some of the operating manuals list the necessary protective equipment and recommended products, so it's a good idea to look at those as well.
-

I’ll check. First of all, what is the relationship between the protective equipment and the current value?
-

OK. First, let me explain the types of protective equipment. Here's an image of the protective equipment in use.
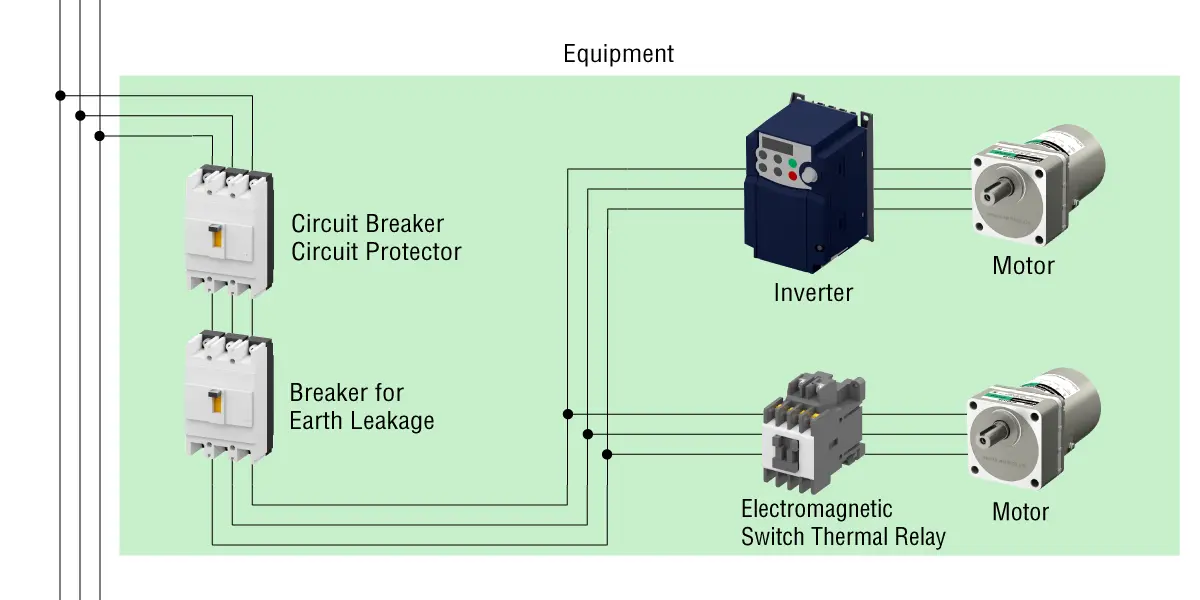
| Circuit Breaker Circuit Protector |
Breaker for Electric Leakage | Electromagnetic Switch Thermal Relay |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose of Protection | Damage caused by overcurrent in electric wires and circuits | Electric shock and fire due to ground fault | Motor burnout due to overcurrent |
- When using an inverter, use a high-frequency-capable breaker for earth leakage. For details, please refer to the operating manual of the inverter.
-

There are many different types of protective equipment. I heard that the current value that needs to be checked differs depending on the protective equipment, but which value should I look at?
-

I've tried organizing it. Look at this table.
| Circuit Breaker Circuit Protector |
Breaker for Electric Leakage | Electromagnetic Switch Thermal Relay |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated Input Current | ● | ● | |
| Inrush Current | ● | ||
| Instantaneous Reversing Current*1 | ● | ||
| Locked-Rotor Current | ● | ||
| Leakage Current | ● |
-

Thank you! There are many ○○ currents.
-

Can you explain the differences?
-

The rated current is the value when the unit is rotating at the rated torque and the rated speed. But other than that, I’m not sure...
-

I've also summarized the currents for each.
| Significance of Current | |
|---|---|
| Rated Input Current | Current value when rotating at rated torque and rated speed |
| Inrush Current | Current flowing at startup of motor |
| Instantaneous Reversing Current*1 | Current that flows during instantaneous bi-directional operation of reversible motor |
| Locked-Rotor Current | Current flowing when the shaft is locked |
| Leakage Current | Current flowing out of an insulated point or path |
-

I got it! However, I don't understand why the data other than the rated current is needed when selecting each protective equipment....
-

I see. I'll explain.
Let’s start from the circuit breaker and circuit protector. Both of these equipment are used to detect and prevent the flow of overcurrent due to some kind of trouble. I wonder if you can imagine how to use the rated current value to determine if it is overcurrent or not. -

Yes. Apart from that, why are inrush current and instantaneous reversing current values required?
-

Inrush current and instantaneous reversing current are currents that are larger than the rated current for a short period of time. This is not abnormal, so you'll need to select a protective equipment to prevent it from being cut off by a momentary high current. Due to the characteristics of circuit breakers and circuit protectors, there is basically no problem if customer select them based on their rated current values, but just to be sure, you should also pay attention to the inrush current and instantaneous reversing current.
-

If you don't choose one that doesn't react when there is inrush current and instantaneous reversing current, it means that the motor will stop immediately. So we need to ascertain the three currents and select protective equipment that only works when there is an overcurrent.
-

That's right, Vex. Next, I'll explain about breakers for electric leakage.
-

Yes, please.
-

When a motor is used with a circuit, this equipment detects leakage from the circuit and shut down the power supply. Even in a normal circuit, there is always a trace amount of leakage current, so the leakage current value is used to determine if there is leakage.
-

I see, so leakage current does not only flow when there is a failure. Therefore, it's necessary at the time of selection.
-

That's right. And finally, electromagnetic switches and thermal relays. I wonder, did you know that the KII Series has a built-in thermal protector?
-

Of course I do! If the motor heats up above a certain temperature due to overload, etc., it will automatically stop.
-

That's right. An electromagnetic switch and thermal relay have the same purpose, which is to shut down the power supply if the motor is locked and a large current flows. Therefore, it is necessary to select so that it will not operate at the rated current, and will be cut off by the current when it is locked.
-

I see. I understand.
-

I'm sure you can answer the question about the protective equipment, can't you, Vex?
-

Let's see... Where did you find these current values?
-

You know that every product has a rated input current value in its catalog specifications. When selecting protective equipment for an AC motor, refer to FAQ "I Am Trying to Select a Breaker to Combine With an AC Motor. Please Tell Me the Current Value Flowing Through the Motor." to find the value.
-

It looks like you can perfectly select an AC motor by referencing the FAQ.
-

The inrush currents for products other than AC motors are listed in the Technical Data.
-

I'll check it out!
-

This time, you can answer the question about the protective equipment, can't you?
-

Yes, I can!
- *1
- Instantaneous reversing current is required only when using an AC motor reversible motor.