Service Life: Service Life of Cooling Fans
Cooling fan life represents the condition in which the fan's capability to generate air flow has deteriorated due to continuous operation over a certain period of time, or the fan can no longer be used due to significant noise.
Service Life of Cooling Fans
- ①
- Rotation life - Life as defined by certain value deterioration in fan rotation speed
- ②
- Sound life - Life as defined by certain increase in noise
The rotation life in ① can be easily measured, and the factors involved can be clearly specified numerically. This is usually what is meant when referring to life.
Sound life in ②, on the other hand, is defined by an increase in decibel level, while determining exactly what amount of increase marks the end of sound life is determined by the user's judgment. Moreover, fans can still meet the operating conditions even after reaching the predetermined increase level in noise. In short, there are generally no specific references or lifetime.
Oriental Motor defines the cooling fan life by ① rotation life; a fan is judged to have reached the end of its life when speed drops to 70 % of the rated speed.
Cooling Fan Bearing Life
Cooling fans use a ball bearing. The following explanation applies to the life of a ball bearing. Since the load applied to cooling fan's bearings is negligible, life of a cooling fan is determined by the deterioration of the grease in the bearings.
Since the cooling fan's operating and starting torques are already smaller than those of a power motor, lack of lubrication due to grease deterioration will cause the starting and dynamic torques of the bearing to increase excessively, which may prevent the fan from starting. Deterioration of grease also increases the noise generated by the bearings, further affecting the life of a cooling fan.
Grease life is given by the following formula:
- t
- Average grease life
- K1, K2, K3, K4
- Constant determined by grease
- Nmax
- Maximum number of rotations allowed by grease lubrication
- n
- Rotation speed of bearings
- T
- Operating temperature of bearings
As indicated by the above formula, Nmax is predetermined by the bearings, so grease life depends on the temperature and rotation speed of bearings. However, Oriental Motor's products are designed so that the bearing life is only minimally affected by their rotation speed. \(\displaystyle \frac{n}{N_{max}}\) is a constant value, which means that the grease life is determined by temperature.
Estimated Life
This is the life estimated by the grease life formula for bearings (ball bearings).
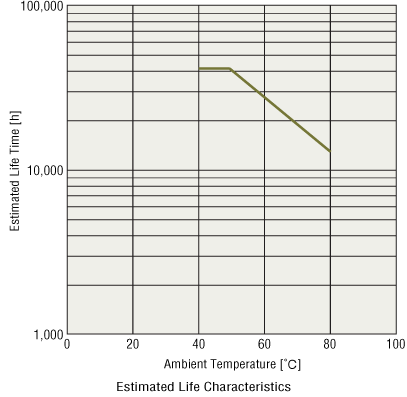
Estimated Life Characteristics
The figure below gives the estimated life characteristics of a cooling fan. (Example: compact AC input cooling fan MU1238A type)
This graph estimates the life of the bearing using the formula for bearing grease life based on actual measurements of temperature rise of the cooling fan bearings at the rated voltage.
Expected Life
It indicates that at least 90 % of the fans will satisfy the following criteria when the acceleration test is performed at the operating ambient temperature's upper limit value.
Criteria
- Rotation Speed (at rated voltage): 70 % min. of rated value
- Input Current (at rated voltage): 130 % max. of rated value